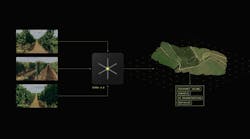
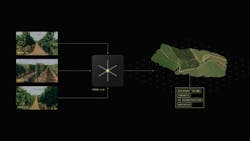
Autonomous robots in the agriculture sector heavily rely on various sensors to navigate and execute tasks efficiently. To create a more cohesive system with these sensors, Stereolabs – a developer of vision-based sensing technology – created Terra AI, a general-purpose artificial intelligence (AI) technology.
Through its use of artificial intelligence, the Terra AI technology enables new approaches to sensor integration, volumetric perception, and computational capabilities to improve visibility, and thus safety and precision, of robots and other autonomous vehicles used in agriculture as well as a range of other industries.
According to Cecile Schmollgruber, CEO and co-founder of Stereolabs, Terra AI consolidates the functionalities of multiple specialized sensors into fewer, more versatile sensors or cameras. “This integration means that the same cameras can perform tasks like surround vision, obstacle detection and high-resolution analysis, which were previously handled by separate devices,” she said.
This approach offers benefits such as cost-effectiveness, simplified management and increased reliability. “Reducing the number of sensors needed for autonomous robots directly translates into lower costs,” she said. This is particularly beneficial for scaling operations where the cost of equipping numerous robots can add up.
With a unified vision platform, she said the complexity of managing and maintaining multiple sensors is significantly reduced. “This simplification leads to easier integration, troubleshooting and updates,” said Schmollgruber. “A single, well-integrated system is often more reliable than a multi-sensor setup, as it minimizes potential points of failure and compatibility issues between different types of sensors.
“Terra AI represents a strategic shift towards a more integrated, efficient and cost-effective multi-camera vision system for autonomous robotics, similar to ADAS [advanced driver assistance systems] for cars,” she added.
READ MORE: Harvesting the Benefits of Autonomous Agricultural Machinery
Data Fusion Creates Better 3D Models
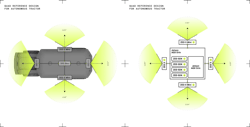
Terra AI utilizes multi-camera setups that cover a 360-degree area to generate a 3D model of the environment. “By fusing this data in time and space, Terra AI generates a complete 3D model of the environment with higher confidence,” Schmollgruber said.
This helps deliver benefits such as higher accuracy in depth and motion estimation; increased redundancy — if one camera fails or encounters issues, the others can continue providing in-depth information; robustness to occlusions; and versatility and flexibility — multi-view setups offer greater flexibility in camera configurations, allowing for customization of the camera placement according to specific application requirements.
Benefits of Simultaneous Processing and Low-Power Embedded Computers
Terra AI addresses the challenges associated with managing multiple independent cameras by streamlining the process and integrating inputs from all cameras. This reduces computational load, enhances system efficiency, and provides a unified and comprehensive view of the robot's surroundings.
“First, managing several cameras independently demands significant compute power,” Schmollgruber said. “Each camera functions as a separate unit, requiring individual processing, which can strain the system's resources. Then, multiple cameras operating independently can lead to a fragmented view of the environment. This disjointed perception can impede the robot's ability to make cohesive decisions and react to its surroundings effectively.”
Terra AI's simultaneous processing benefits low-power embedded computers by optimizing computational tasks for multi-camera setups, thus significantly improving the robot's ability to navigate safely and perform tasks autonomously. “This unified perspective is essential for advanced applications where situational awareness is critical,” she said.
READ MORE: Emerging Sensor Design Requirements for Embedded Vision
Enhanced Perception and Navigation Capabilities with NVIDIA Jetson Platform
Terra AI has been optimized to operate on NVIDIA Jetson platforms, leveraging the unique hardware capabilities and architectural strengths of NVIDIA Jetson GPUs (graphics processing unit). “The Jetson platforms, known for their powerful GPU-based processing and efficiency in handling AI and machine learning tasks, provide an ideal environment for Terra AI to function at its peak,” Schmollgruber said.
This results in enhanced performance, especially in tasks requiring real-time processing and deep learning applications, ultimately enhancing overall perception and navigation capabilities of autonomous robots in terms of scalability and cost-effectiveness. Integration with a platform like NVIDIA's is crucial for robotics applications where rapid data processing and decision-making are essential, she said.
Modular Architecture Eases Integration
Terra AI's modular architecture allows seamless integration with various camera setups, offering manufacturers extensive flexibility and scalability. From basic to complex robotic systems, Terra AI can be tailored to meet diverse application requirements, making it adaptable to a wide range of hardware configurations.
“Depending on the specific requirements of our customers, Terra AI demonstrates exceptional versatility,” Schmollgruber said. “It is capable of operating efficiently with a single front-facing camera or can be scaled up to work with multiple cameras positioned around the machinery for comprehensive coverage. This adaptability allows Terra AI to cater to a broad spectrum of applications, ranging from basic to complex robotic systems, by customizing its functionality to meet the precise needs of different scenarios.”
READ MORE: Opportunities and Challenges for Fluid Power in Automation
Addressing Autonomy Challenges
One of the major challenges in using multi-camera systems for robotics is camera calibration. “Properly calibrating and aligning multiple cameras is crucial for accurate depth perception,” said Schmollgruber. “Misalignment can lead to distorted or inaccurate environmental models.”
Terra AI addresses this challenge through advanced calibration techniques developed over 13 years, ensuring precise alignment of images even in challenging environments such as agriculture, construction and logistics where vibrations, changes in temperature and shocks are frequent.
This approach to sensor integration, volumetric perception, computational capabilities and modular architecture presents opportunities for the agriculture industry. Terra AI offers a scalable way to deploy autonomous machines — such as tractors, mowers, utility vehicles, AMR (autonomous mobile robots), robotic arms and more — by leveraging low-cost cameras combined with an NVIDIA Jetson Orin GPU to provide a panoramic 360-degree surround view.
With its potential to enhance efficiency, reduce costs and improve reliability, Terra AI stands as a driving force in the advancement of autonomous robotics in agriculture, helping to shape a more sustainable and tech-forward industry landscape.
“As we further collaborate with manufacturers and system integrators, our latest Terra AI technology aims to address a growing need for a more open, adaptable and scalable vision platform delivering 360-degree perception and driving true autonomy,” said Schmollgruber. “Terra AI will allow companies across industries to invest in autonomous robotics at scale, helping them run their operations with greater efficiency and precision at [a] lower cost.”