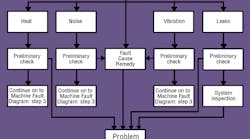
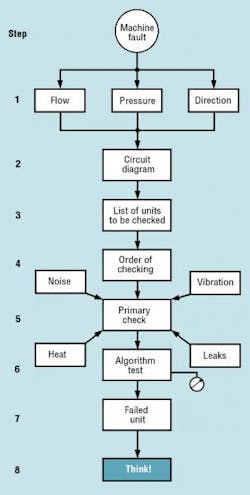
The troubleshooting process must follow a logical sequence. This rule cannot be overemphasized. A Machine Fault Checklist, Figure 1, provides an orderly plan to determine the cause or causes of a machine’s a malfunction.
Initial troubleshooting procedure
Step 1. Any fluid power actuator is operating improperly if you notice:
- no movement
- movement in the wrong direction
- erratic movement
- incorrect speed
- creep (drift)
- incorrect sequence, or
- incorrect force.
Whatever the reason, the problem should be defined in terms of flow, pressure, or direction.
Step 2. Using the circuit diagram, identify each component in the system and determine its function.
Step 3. Compile a list of components that could possibly cause the problem. Thus, slow actuator speed can be related to flow, even though low pressure may be indicated. Remember that a leaking or improperly adjusted relief valve (i.e., a pressure control valve) could affect flow to the actuator.
Step 4. Arrange the list of components in rough order of priority based on your past experience and the ease with which they can be checked.
Step 5. Conduct a preliminary check of each component on the list. Look at installation, adjustment, signals, etc. Also determine if any component shows abnormal symptoms such as excessive temperature, noise, vibration, etc.
Step 6. If the preliminary check reveals no obviously faulty component, conduct a more exhaustive repeat test of each using additional instrumentation – without removing any unit from the system.
Step 7. The instrument checks should identify the faulty component. Someone then must decide whether to repair or replace.
Step 8. Before re-starting the corrected machine, stop and consider the cause and consequence of the failure. For example, if the failure was caused by contaminated or over-heated fluid, you should anticipate additional component failures until you take remedial action against that underlying cause. If a pump failed mechanically and debris entered the hydraulic system, the system should be thoroughly cleaned before a new pump is installed and operated.
Again, think about what caused the failure and its potential consequences.
Coming next: Chapter 3: Use Your Senses to Begin the Troubleshooting Process