When Belle, the elephant matriarch at the Oregon Zoo, Portland, needed foot surgery, Allied Power Products, in nearby Beaverton, came up with a way to place the 6900-lb pachyderm on her side on a padded pneumatic mattress so veterinarians could perform a two-hour operation.
Positioning the elephant posed a challenge to Allied Power Products, which specializes in custom-designed winches and hoists. Not only did she have to be lifted, she had to be rolled on her side and lowered — and then rolled back and lifted to her feet after surgery. As Allied President Bob Peterson said, “This wasn’t a hunk of steel or a load of concrete. You can lift 500-ton pier forms all day, but this was an irreplaceable, living creature. It was an absolute thrill to be part of such a special project, but our equipment had to work — period — or the surgery couldn’t have been done. There was no allowance for a miscue or redo. We couldn’t regroup and try again the next day.”
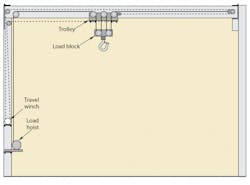
Further complicating the situation was a ceiling height that limited headroom to only 13 ft above the 8 ft tall elephant. Allied’s solution was a 2-winch system and a custom inverted trolley that ran inside the supporting I-beams at the ceiling, rather than below them, to provide maximum lifting clearance. An 8000-lb capacity hydraulic winch was used to drive the trolley back and forth. A 5000-lb capacity hydraulic hoist, rigged in a hammerhead with four parts of line through a special load block (shown at left), lifted the hefty animal. With this rig, the hook remains at the same height as the trolley moves. An existing hydraulic power unit — normally used to open and close the doors in the elephant house — supplied 1500- to 1800-psi pressurized fluid to the winches.
Naturally inquisitive elephants often are unwittingly destructive, so protecting the equipment was another consideration. By mounting the winches between beams on a wall and keeping exposed components to a minimum, the possibility of the elephant damaging parts of the system was reduced.
Bob Peterson operated two lever-actuated directional valves to operate the winches on surgery day. He lifted Belle about 8 in. off the floor, then moved her to the edge of the surgery mat. While keepers held her right-side feet stationary, he slowly moved the trolley farther to the right and simultaneously lowered the hook to roll her gently onto her side.
For more information on hydraulic, pneumatic, and electric hoists and systems, visit www.alliedpower.com.