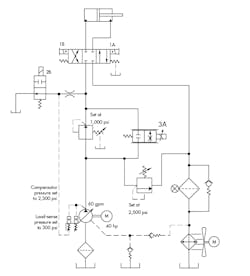
A previous installment of Troubleshooting Challenge referred to the accompanying circuit. The problem was that the hydraulic system would not go to the 300-psi standby pressure when solenoid 2B was de-energized. The problem was found to be contamination plugging the control orifice.
The user ran into a problem after about four years of good performance from the system. The pump was replaced as a preventive measure when technicians found the shaft seal was starting to leak. Then a new problem cropped up: The speed cylinder was the same until system pressure exceeded 1,000 psi, which caused the pressure-reducing valve to close. The machine had an electronic display that showed the electrical signal to the proportional valve, and it was the same as before the pump was changed.
Any idea what was causing the problem?
Find the Solution
Think you know the answer to this month’s problem? Submit your solution via email. All correct answers submitted by March 19, 2018 will be entered into a random drawing for a $50 gift card. The winner will be notified, and his or her name will be printed in a future issue. Only one gift card will be awarded to any participant within a calendar year.
Congratulations to Joel Mekkes, of Lincolnshire, Ill., whose name was chosen from those who correctly answered last month’s challenge. A $50 gift card is in the mail to him.
Solution to Last Month’s Challenge:
Blown shaft seals typically in worn pumps with high case flow or case drain lines restricted or blocked. When inspecting the reservoir for clues, technicians found water had collected in the bottom of the reservoir, and the case drain line terminated below the water line. The inlet to the pump inlet, however, was up higher. Consequently, leaving the machine outdoors at temperatures below freezing blocked the case drain line when the water froze.
Reservoirs for outdoor use should be sealed, or else use a desiccant breather or other means to keep moisture out of the reservoir.